XB2MIDI
Map XBOX Controller Inputs to MIDI Messages, MIDI Macros, Chords, and more!
Project Overview
XB2MIDI is a Windows desktop application that turns a wired Xbox 360 controller into a flexible MIDI controller. It maps controller inputs to MIDI messages, macros, chords, and more for use with DAWs, VST instruments, and automation. With multiple mapping modes, from straightforward one-to-one mappings to chord and arpeggio workflows, you can create, perform, and sequence musical ideas directly from a gamepad.
Introduction Video
Build Download
[ Coming Soon ]
Backstory
Mapping Modes
XB2MIDI features five distinct mapping modes, each designed for different use cases. Each mode provides unique ways to transform controller inputs into MIDI data.
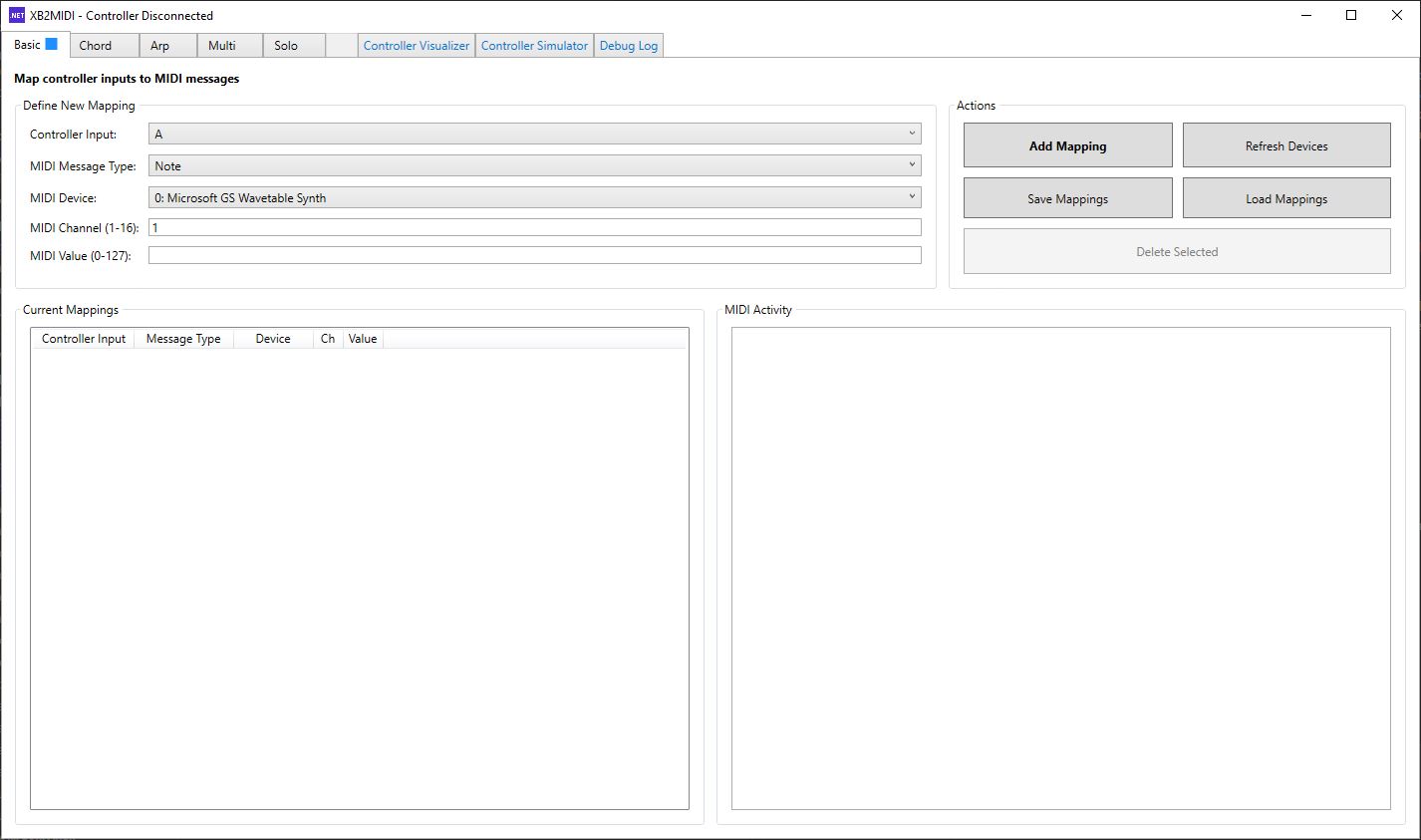
Basic Mode
Basic Mode is XB2MIDI’s direct 1:1 mapping workflow. Map any Xbox 360 controller input (buttons, D-pad, sticks, triggers) to a single MIDI output (Note, CC, or Pitch Bend), choose the target MIDI device and channel, and save or load full presets for repeatable sessions. Pitch Bend works especially well with continuous inputs like joystick axes and triggers for smooth, expressive control. With MIDI routing (for example loopMIDI), those mappings can drive DAWs, VST instruments, effects, and automation, with a live MIDI Activity view for quick validation.
Basic Mode Demo
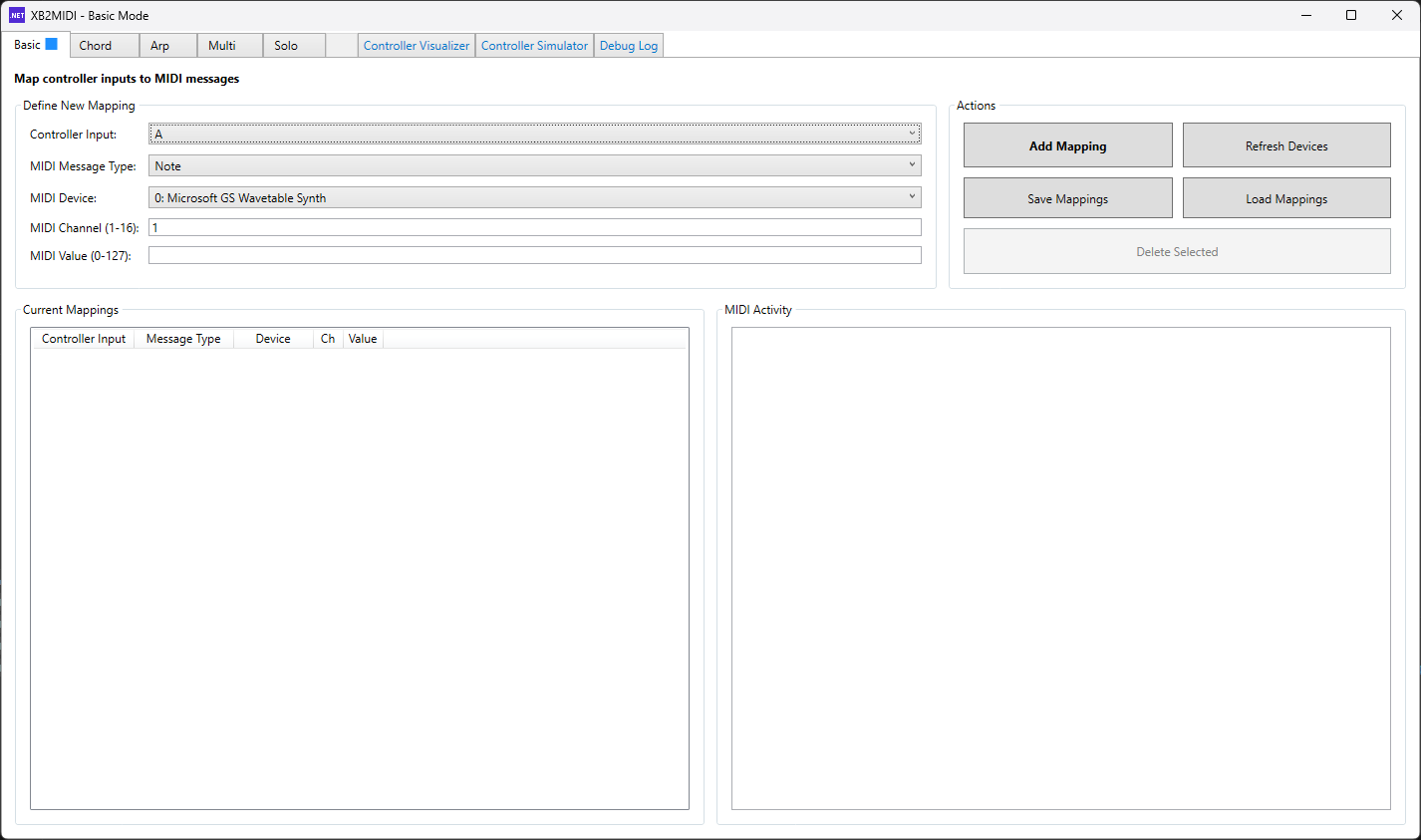
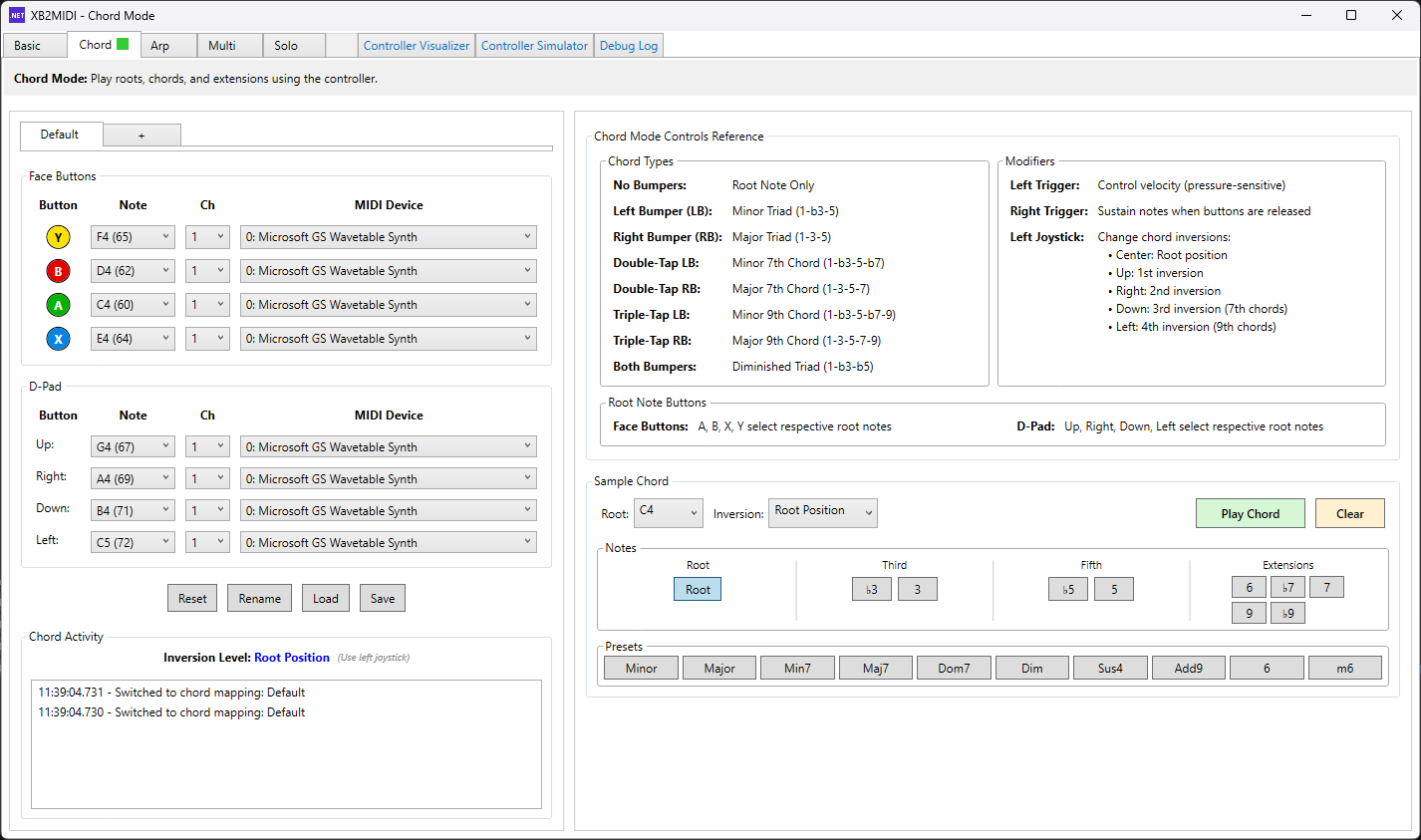
Chord Mode
Chord Mode turns the controller into a chord keyboard built around eight root-note buttons. The face buttons and D-pad provide eight assignable root notes, which can be mapped to a key’s scale degrees or to any custom note layout. Pressing a root button alone plays the root note. Holding RB while pressing a root plays a major triad, and holding LB plays a minor triad. Chord extensions are triggered by tap patterns: double-tap RB/LB for major 7th / minor 7th, and triple-tap RB/LB for major 9th / minor 9th. Chord inversions are selected with the left stick before triggering the chord: center is root position, up is 1st inversion, right is 2nd inversion, down is 3rd inversion, and left is 4th inversion when applicable. For expression, left trigger depth controls attack (velocity) and right trigger depth controls sustain. This makes it easy to send multi-note MIDI bursts into a DAW or VST so you can actually perform chords on an instrument, trigger custom multi-note “macros” you define on the DAW side, or quickly stamp chords into a MIDI piano roll (for example in FL Studio).
Chord Mode also supports multiple mappings at once via tabbed layouts (including the “+” to add new mappings), full save/load preset workflows, and an activity log for debugging. The right-side panel provides a built-in reference for the full button-combo scheme, and the bottom-right chord tester lets you audition chord types and extensions using Windows built-in tones before committing to a mapping.
Chord Mode Demo
In-Development Modes
These modes expand the mapping possibilities beyond static notes and chords, though they are still in active development:
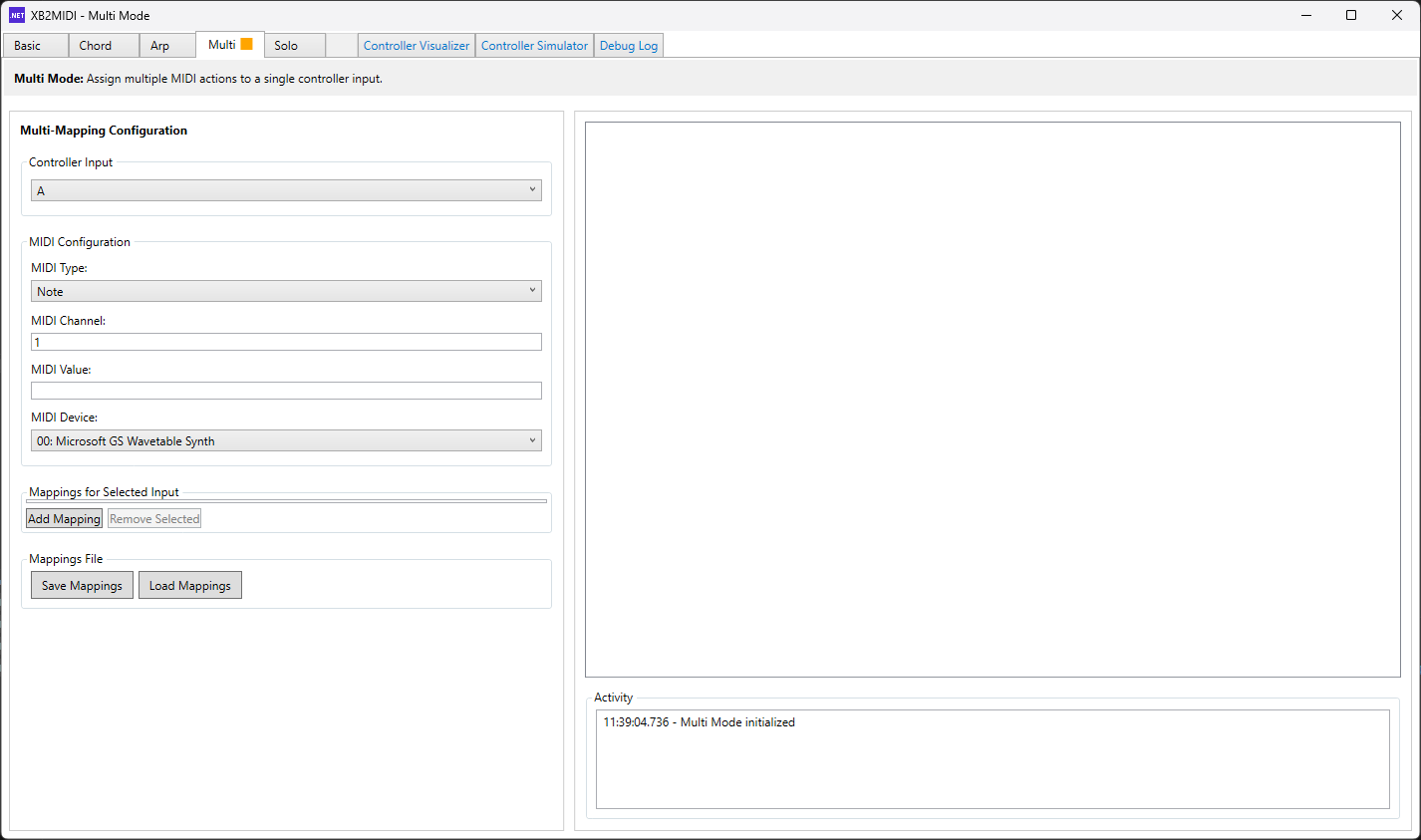
Multi Mode ✓ Mostly Complete
Multi Mode enables multiple MIDI messages to be triggered from a single controller input, functioning as a macro system. A single button press can send multiple notes across different channels and MIDI devices simultaneously, enabling complex orchestration and layered sound design. This is essential for building intricate musical arrangements without manual sequencing.
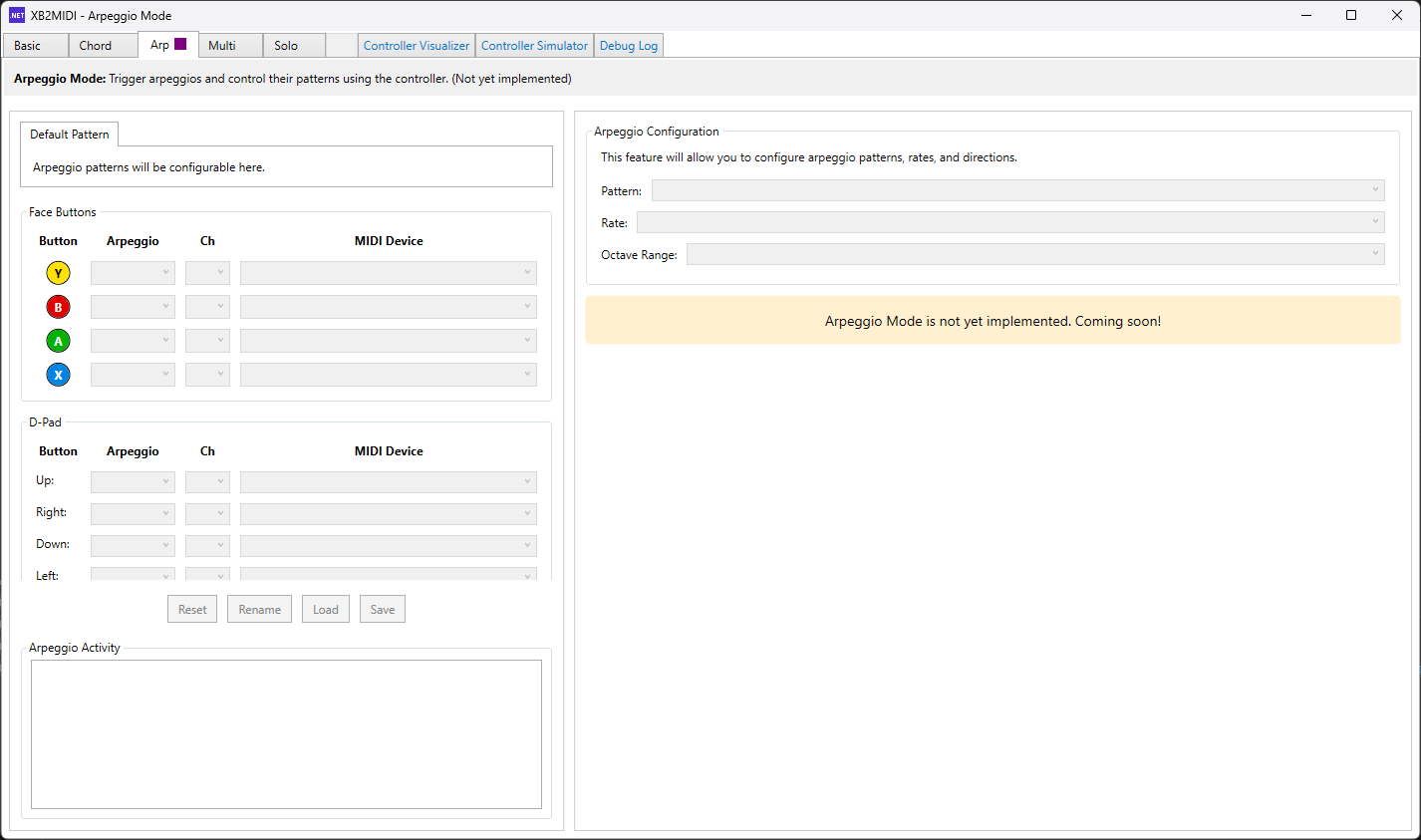
Arpeggio Mode 🚧 In Development
Arpeggio Mode generates automatic note sequences (arpeggios) based on input patterns. Rather than playing individual notes, a button press triggers a pre-configured pattern of notes in sequence, with control over playback speed, pattern type, and direction. This mode is pending implementation and will provide powerful melodic pattern generation for dynamic performances.
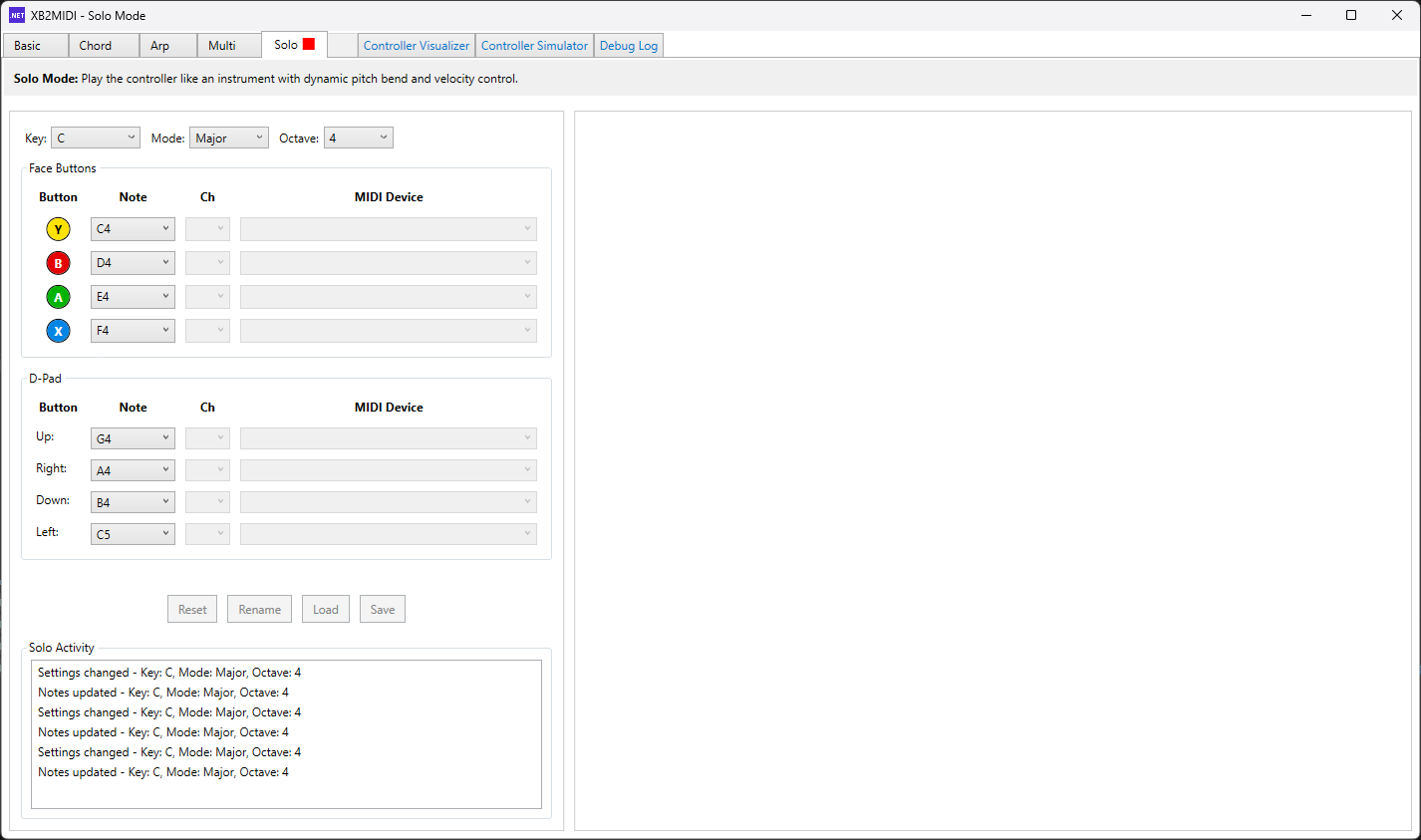
Solo Mode 🚧 In Development
Solo Mode is designed for continuous melodic control with smooth pitch bending. Using analog trigger values from the controller, Solo Mode allows you to play single notes with expressive pitch bend control for slide-like transitions and vibrato effects. This mode is pending completion and will enable natural, violin-like solo performances from your controller.
Multi Mode Demo and In-Dev Mode Overview
Technologies Used
Core Technologies
- C# with .NET 9.0
- WPF (Windows Presentation Foundation)
- SharpDX.XInput 4.2.0
- NAudio 2.2.1 (MIDI output)
Development Tools
- Visual Studio 2022
- Visual Studio Code / Rider
- Git / GitHub
- Windows 10+ (target platform)
Architecture
XB2MIDI employs a robust, layered architecture built on the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) pattern, combined with service-oriented design principles and polymorphic type hierarchies. This design separates concerns across input handling, MIDI output, business logic, and UI presentation, enabling testability, extensibility, and clean mode switching across five distinct mapping implementations.
Models Layer
The Models layer implements core business logic and manages state with polymorphic abstractions for extensibility.
MappingManager Hierarchy (Polymorphic Strategy Pattern)
Each manager handles its own HandleControllerInput(ControllerInputEventArgs)
logic, JSON serialization/deserialization (with mode-specific file extensions like
.basic.json, .chord.json), and mapping persistence. This polymorphic design allows new modes
to be added by simply inheriting MappingManagerBase without modifying existing code—a key
advantage for maintaining clean architecture as the application evolves.
MappingManagerBase
Abstract base class defining the contract for all mapping strategies. Each mode inherits from this base and implements mode-specific logic.
BasicMappingManager
1:1 input-to-MIDI mappings (notes, CC, pitch bend)
ChordMappingManager
Multi-note chord generation with inversions and extensions
MultiMappingManager
Single input triggering multiple simultaneous MIDI messages (macro system)
ArpeggioMappingManager
Sequenced note patterns with tempo and direction control
SoloMappingManager
Expressive single-note melody with pitch bend modulation
Input Handling & State Management
This layer captures and normalizes Xbox controller input, providing clean event-based access to physical device state while maintaining thread safety and connection reliability.
XboxController
Wraps SharpDX.XInput with thread-safe polling, deadzone normalization, and connection
state tracking. Fires InputChanged events for state deltas and
ConnectionChanged events for hot-plug detection. Runs on a background
thread to avoid UI blocking.
ControllerInputEventArgs
Custom event args encapsulating input name, type (button, stick, trigger), current value, and context
MidiMapping
Data model representing a single controller-to-MIDI binding (controller input, MIDI device, channel, message type, target note/CC)
MappingMode & ControllerMode
Enumerations defining operational states (Basic, Chord, Multi, Arpeggio, Solo)
MIDI Device Lifecycle Management
Sophisticated device connection management ensures the application gracefully handles device hot-plugging, unavailability, and reconnection scenarios without crashing or losing state.
MidiOutput
Manages device connections with sophisticated fallback logic, ensuring reliable MIDI device handling and graceful degradation
Device Handle Management
Maintains a dictionary of open MidiOut handles (via NAudio)
Device Verification
EnsureDeviceExists() verifies device availability before sending
messages; attempts reconnection if the device was previously open
Safe Availability Checks
IsDeviceAvailable() performs safe availability checks without throwing
exceptions
Fallback Logic
If a mapped device becomes unavailable, automatically routes to the first available device and logs the event
Hot-Plug Handling
Gracefully handles MIDI device hot-plugging without crashing or losing state
Views Layer
Views are XAML-based WPF user controls with minimal code-behind, using data binding and value converters to render UI without business logic. The view layer includes mode-specific controls, real-time controller visualization components, and helper dialogs.
Mode Views
BasicMappingView, ChordMappingView, MultiMappingView, ArpeggioMappingView, SoloMappingView. Each view binds to its ViewModel and renders mode-specific controls
Controller Visualization
BaseControllerVisualizer (abstract), ControllerVisualizer (real-time display of physical input state), InteractiveControllerVisualizer (simulated input from keyboard)
Auxiliary Views
ChordModeReferenceView (button-combo legend), ChordSamplerView (chord preview tester), MainWindow (tab host)
Value Converters
StringToVisibilityConverter (toggle UI elements based on string state), MidiTypeToEnabledConverter (enable/disable fields based on MIDI message type)
View Models Layer
ViewModels implement INotifyPropertyChanged and expose data via
ObservableCollection<T> for two-way binding, bridging the gap between Models
and Views. Each mode has dedicated ViewModels that coordinate with their corresponding
MappingManager and translate user interactions into business logic.
Mode-Specific ViewModels
Each of the five mapping modes has a dedicated ViewModel that coordinates with its corresponding MappingManager, exposes ObservableCollections for UI binding, and implements ICommand-bound methods for user interactions:
BasicMappingViewModel
Coordinates with BasicMappingManager for 1:1 MIDI mappings
ChordMappingViewModel
Manages chord mode interactions with inversions and extensions
MultiMappingViewModel
Handles multi-message macro system mappings
ArpeggioMappingViewModel
Controls arpeggio pattern sequences and playback
SoloMappingViewModel
Manages expressive single-note melody control
Shared Collections
All ViewModels expose ObservableCollections (Mappings, ActivityLog, MidiDevices, ControllerInputs)
Orchestration & Support ViewModels
MappingTabManager
Orchestrates mode switching, maintains per-mode state, handles tab activation/deactivation, and coordinates persistent storage across mode transitions
ChordSamplerViewModel
Dedicated ViewModel for the chord preview/tester UI, managing chord type selection and Windows sound API playback for audition purposes
RelayCommand Pattern
All ViewModels use RelayCommand (both generic and non-generic) to bind user actions to business logic without code-behind cluttering
Services Layer
Services provide cross-cutting functionality via dependency injection and interface-based contracts, enabling testability, loose coupling, and easy mocking in unit tests. Key services handle MIDI operations and platform-specific dialogs.
IMidiService / MidiService
High-level MIDI abstraction wrapping MidiOutput. Exposes methods like
SendNoteOn(), PlayChord(), and device enumeration with
exception handling
IDialogService / DialogService
Encapsulates WPF file dialogs for open/save operations, enabling mocking in unit tests
Utilities & Support Layer
Utility modules provide reusable functionality for music theory calculations, input normalization, and command patterns used throughout the application.
MusicTheory
Static utility for chord analysis. Determines chord quality (major, minor, dim, sus4, etc.) from note sets, handles inversions and extensions, and generates human-readable chord names
ScaleHelper
Generates scale degrees for chord mode root note assignment
Extension Methods
CollectionExtensions and EventArgsExtensions for common operations
RelayCommand
Generic (RelayCommand<T>) and non-generic implementations of ICommand
for binding UI actions without code-behind
Data Persistence & Configuration
All mappings are persisted as human-readable JSON files with mode-specific extensions and structures. This approach provides several key benefits:
Sharing & Version Control
Easy sharing and version control of presets
Manual Editing
Manual editing and debugging of configurations
Independent State
Independent state for each mode (switching modes preserves previous mode's state on disk)
Preset Files
Preset files for chord collections (.chord.json), basic mappings (.basic.json), and multi-mode macros
Design Principles & Patterns
Separation of Concerns
MVVM cleanly decouples UI from business logic. Models know nothing about Views; ViewModels translate between them via data binding.
Polymorphism & Strategy
The MappingManagerBase hierarchy allows each mode to implement its own input handling strategy without if/else cascades in the main loop.
Dependency Injection
Services (MidiService, DialogService) are injected into ViewModels, enabling mocking and testability.
Event-Driven Architecture
Controller input, MIDI lifecycle, and mode transitions are all event-driven, allowing decoupled communication without tight coupling.
Thread Safety
Input polling runs on a background thread; state updates marshal to the UI thread via Dispatcher to prevent freezing.
Graceful Degradation
MIDI device failures trigger fallback logic and logging rather than exceptions. The application continues to function even if the primary device is unavailable.
Implementation Details
XB2MIDI is built as a scalable, mode-driven MIDI controller application. The core loop continuously polls Xbox controller input via SharpDX.XInput, processes state changes through the active MappingManager, and sends resulting MIDI messages to connected devices via NAudio. Mapping configurations are persisted as JSON files (.chord.json, .mapping.json, etc.) for easy sharing and backup.
Key Features
- Five distinct mapping modes for different use cases
- Multi-device MIDI output support
- Chord preset system with custom .chord.json files
- Real-time controller input visualization
- Integrated controller simulator for testing without hardware
- Persistent mapping storage
System Architecture
- MVVM pattern for clean separation of concerns
- Pluggable MappingManager system for mode extensibility
- Event-driven input polling (no blocking UI)
- Async MIDI device lifecycle management
- Tab-based UI with seamless mode switching
Platform & Requirements
Target Platform: Windows 10 / 11 (64-bit)
Requirements: .NET 9.0 runtime, Xbox-compatible controller (XInput), MIDI device or software synthesizer
Compatibility: Works with any XInput-compliant gamepad (Xbox One, Xbox Series X/S, third-party controllers)
Development Challenges
Real-Time Controller Input Polling
XInput polling must occur at a consistent refresh rate without blocking the WPF UI thread. Polling too slowly introduces input lag; blocking the UI makes the application unresponsive. Additionally, controller connection/disconnection events needed to be detected reliably.
Implemented a background polling thread running on a fixed timer (e.g., 60 Hz) that captures controller state and raises events without blocking the main thread. Used ManualResetEvent patterns to ensure thread-safe state handoffs. Connection status is tracked per-frame to detect hot-plug scenarios.
MIDI Device Lifecycle Management
MIDI devices can be connected or disconnected at any time. If a mapping references a device that is no longer available, the application could crash or silently fail to send MIDI data. Managing open device handles and recovering gracefully from missing devices is non-trivial.
Developed a MidiOutput manager that maintains a dictionary of open MIDI device handles. Before sending a message, the manager verifies the device is available; if not, it attempts to re-open it. If the device is permanently unavailable, a fallback device is used, and the user is notified via the debug log. Mappings are validated on load to warn users of missing devices.
Cross-Mode State Management
With five distinct mapping modes, each with its own state, configuration, and behavior, switching between modes must preserve each mode's state and avoid data loss. The challenge is isolating mode-specific state so changes in one mode don't unexpectedly affect another.
Each mode has its own MappingManager instance with independent state. The MappingTabManager orchestrates switching by pausing the current mode, saving its state to disk, and loading the target mode's state. ViewModels are mode-specific and updated only when their corresponding tab is active. Persistent JSON serialization ensures no data is lost during mode transitions.
Debug Tools
XB2MIDI provides three integrated debug tabs within the application to aid in development, testing, and troubleshooting. These tools offer real-time visualization of controller state, input simulation without hardware, and comprehensive activity logging.
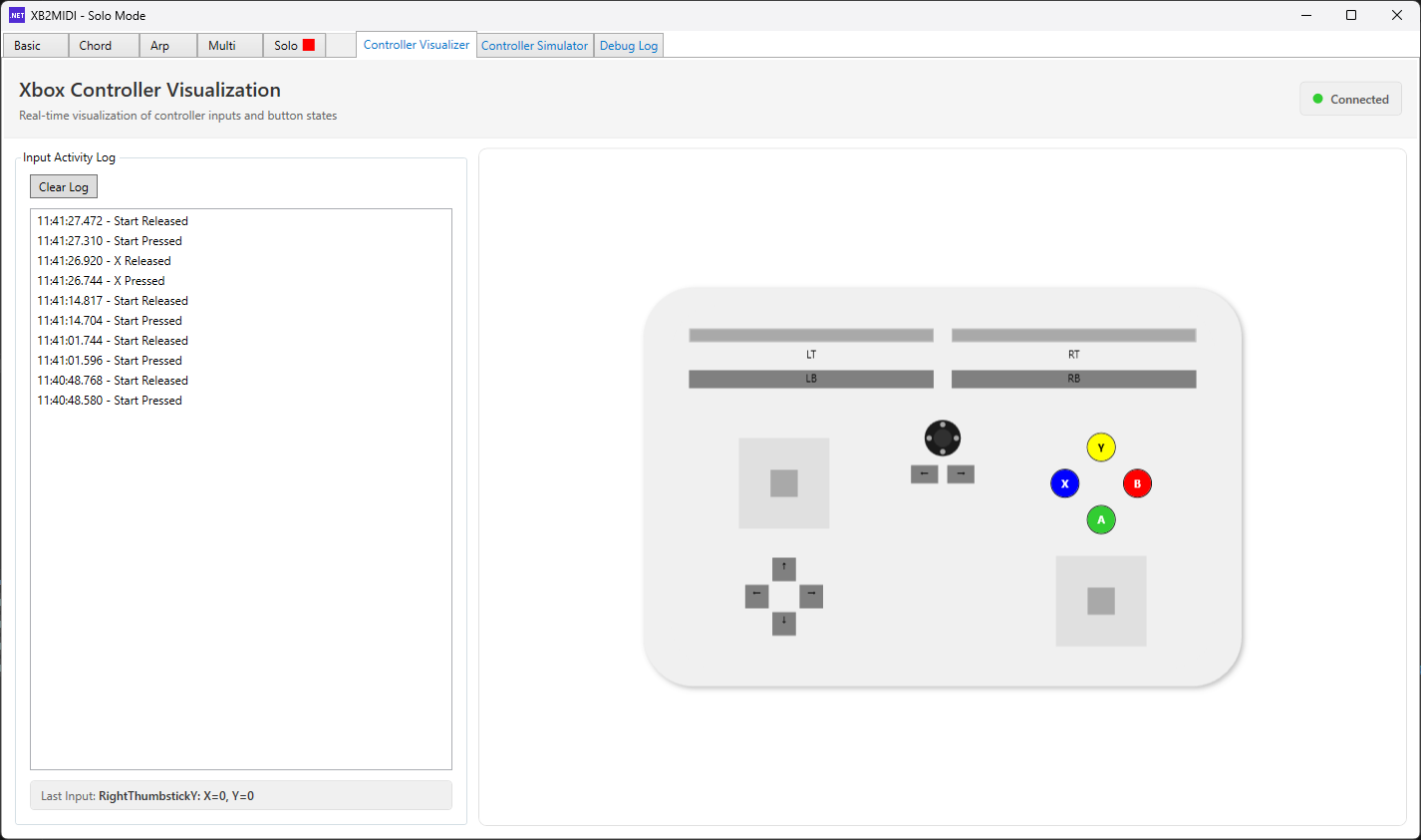
Controller Visualizer
The Controller Visualizer is a real-time on-screen display of your physical controller's input state. As you press buttons, move sticks, and pull triggers on your Xbox controller, the visualizer reflects each input on a graphical controller representation. This is invaluable for debugging input mapping issues, confirming that inputs are being registered correctly, and understanding how your physical movements translate to MIDI messages.
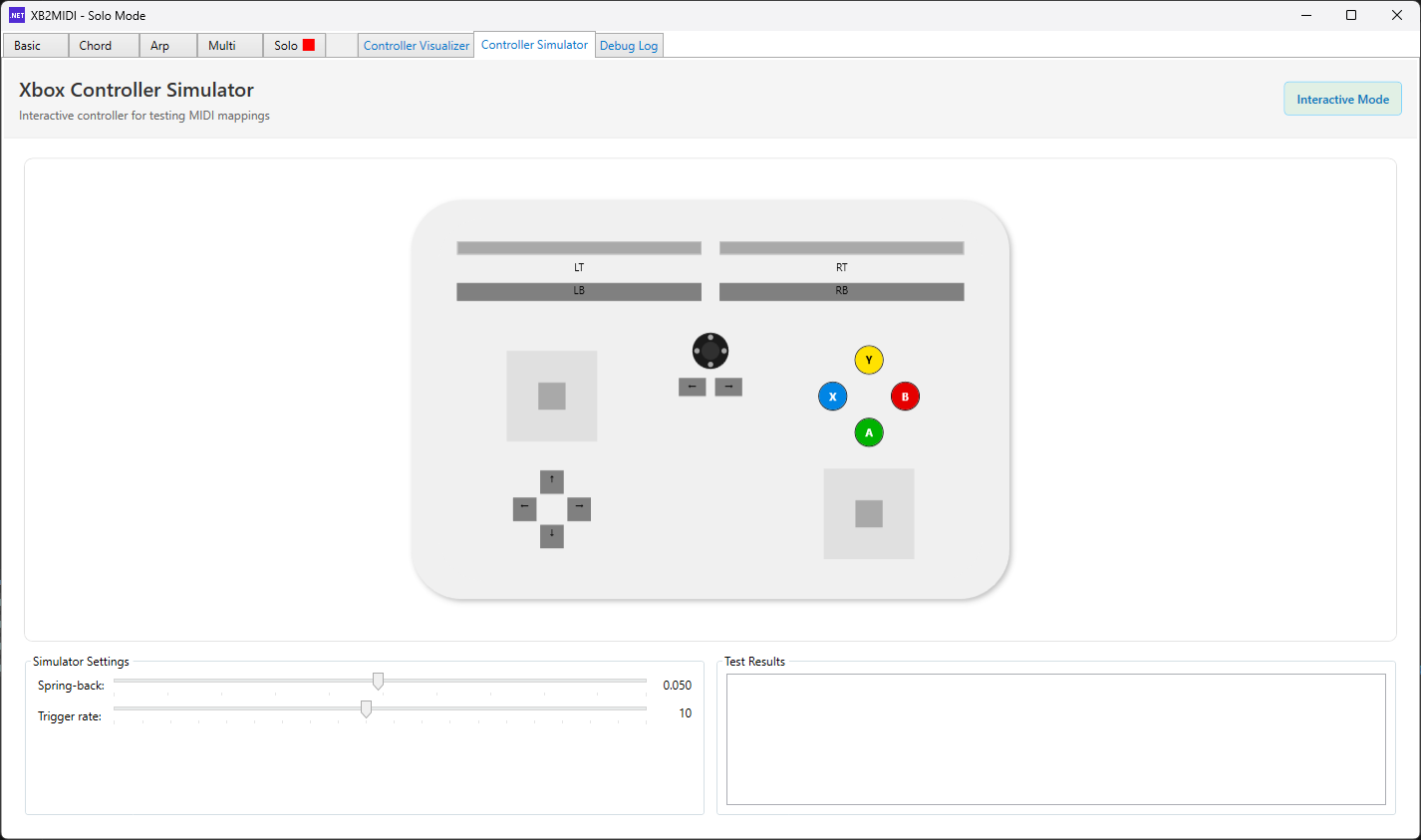
Controller Simulator
The Controller Simulator is both a developer tool and a user-facing feature. It allows you to test and validate mappings without requiring a physical Xbox controller. The simulator replicates controller input by accepting mouse input from your PC, simulating button presses, D-pad directions, and basic analog input (limited to non-combination inputs for developer testing). For users, it provides a way to explore mode features and verify mappings in environments where a controller may not be available.
Controller Simulator Demo
Activity Log & Debug Output
The Activity Log provides a comprehensive, real-time record of all controller inputs and MIDI events. This persistent debug output helps you trace the flow of input through your mappings, identify timing issues, validate that expected MIDI messages are being sent, and diagnose unexpected behavior. The log displays input source, type, value, timestamp, and any associated MIDI output, making it essential for troubleshooting complex mapping scenarios and understanding the complete input-to-output pipeline.
Future Enhancements
MIDI Learn Mode
Implement an automated mapping mode where pressing a controller button automatically assigns it to the MIDI note or CC message currently being played, eliminating manual mapping entry.
Controller Profiles
Save and load multiple configuration profiles, allowing quick switching between different mode setups for different musical genres, games, or use cases.
Complete Arpeggio Mode
Finish implementation of Arpeggio Mode with pattern sequencing, tempo control, and direction options, making it production-ready for generating dynamic melodic patterns.
Complete Solo Mode
Finish implementation of Solo Mode with smooth pitch bend control, vibrato support, and expressive trigger-based modulation for natural, violin-like solo performances.
VST Plugin Wrapper
Wrap XB2MIDI as a VST plugin, allowing direct integration into DAWs (Digital Audio Workstations) for seamless in-session controller mapping without a separate application window.